Reducing Annotation Work in High-FPS Vision Applications with Roboflow
High-speed performance is a must for today's computer vision applications, but it comes with many challenges. These include processing a high volume of frames per second (FPS), which requires not only fast algorithms, but also efficient data storage to handle the large quantities of images being processed in real time.
Traditional annotation methods are often time-consuming and labor-intensive for training machine learning models. In other words, they create bottlenecks that slow down projects from getting done.
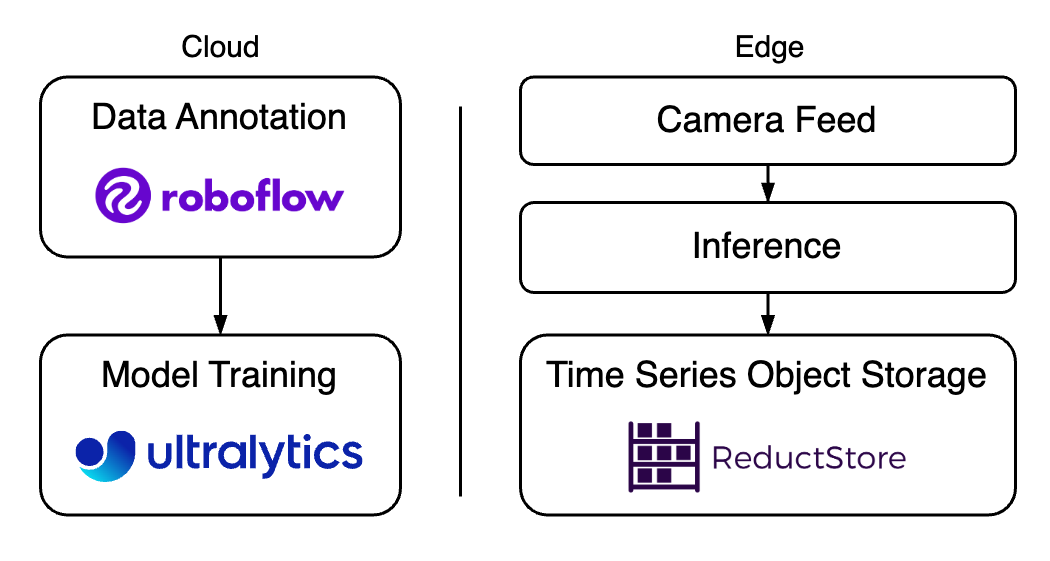
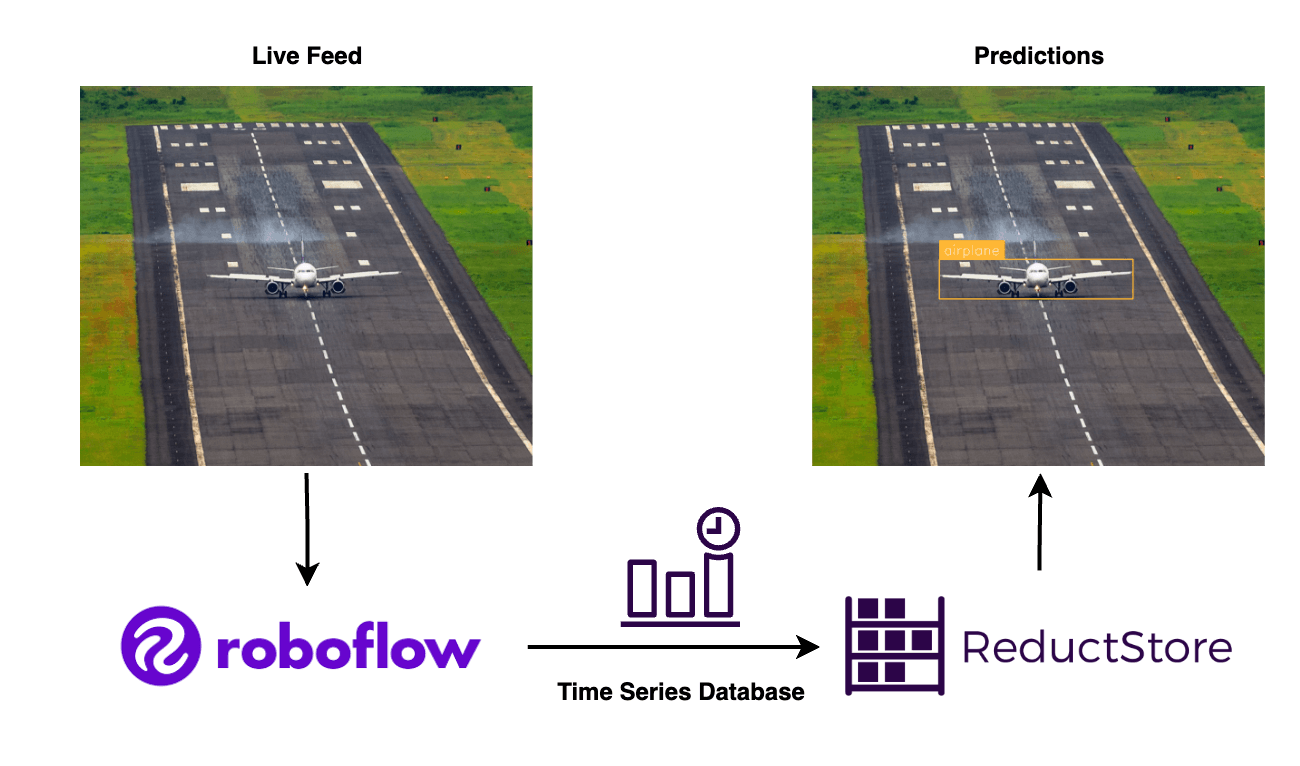
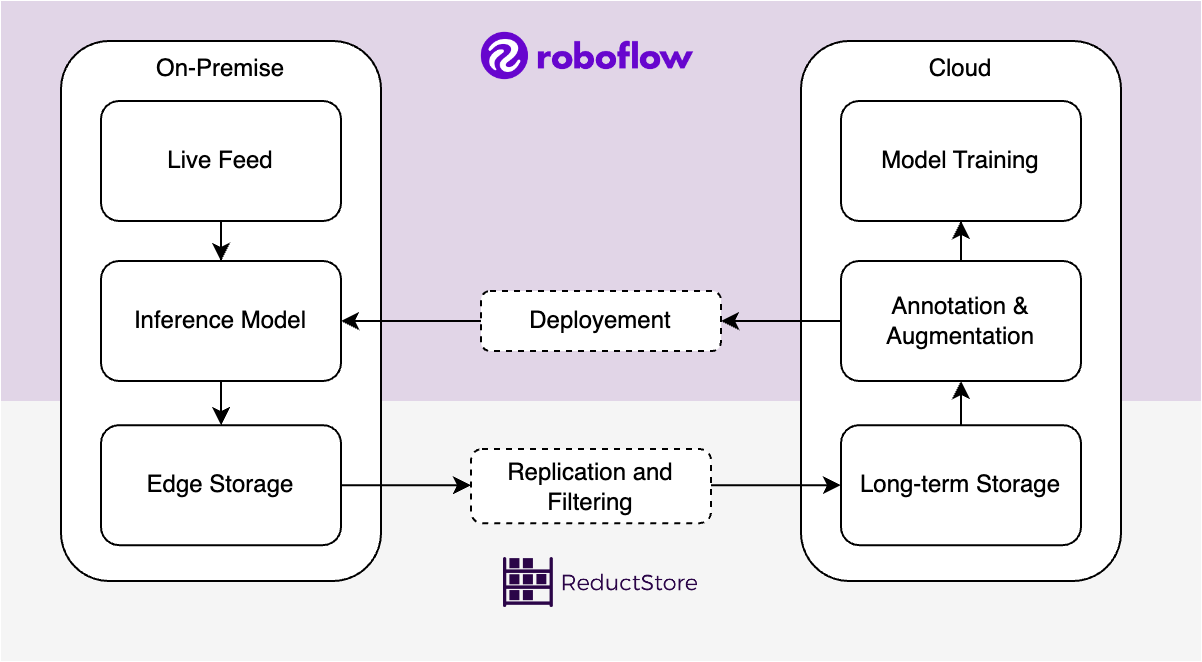
At the same time, Roboflow was designed to address the challenges associated with annotating data, but manually labeling all images is often tedious and unrealistic. In this case, ReductStore can provide the tools to query, filter, and replicate specific images for further annotation and training.
In this article, we'll explain how Roboflow can help reduce the time and effort required to annotate images, and how ReductStore can be used to store and filter important images.