Reducing Annotation Work in High-FPS Vision Applications with Roboflow
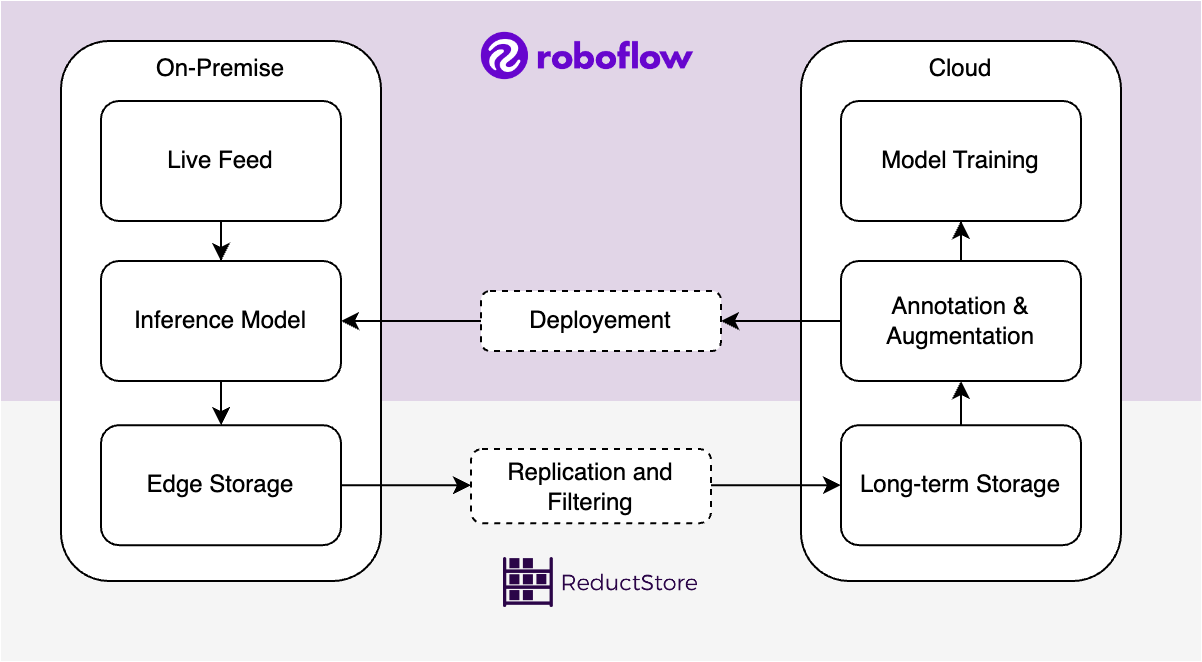
High-speed performance is a must for today's computer vision applications, but it comes with many challenges. These include processing a high volume of frames per second (FPS), which requires not only fast algorithms, but also efficient data storage to handle the large quantities of images being processed in real time.
Traditional annotation methods are often time-consuming and labor-intensive for training machine learning models. In other words, they create bottlenecks that slow down projects from getting done.
At the same time, Roboflow was designed to address the challenges associated with annotating data, but manually labeling all images is often tedious and unrealistic. In this case, ReductStore can provide the tools to query, filter, and replicate specific images for further annotation and training.
In this article, we'll explain how Roboflow can help reduce the time and effort required to annotate images, and how ReductStore can be used to store and filter important images.
High-FPS Computer Vision Applications
Applications such as autonomous vehicles, surveillance, robotics, or even sports analytics often require real-time image processing. These systems can analyze thousands of images at high speed, but the large number of images they process requires an efficient storage and retrieval system to properly handle the load
The requirements for storage and querying images are the following:
- High-performance database that can read and write images quickly.
- Efficient indexing and filtering mechanisms for fast image retrieval.
- Scalable solutions to support storage growth over time.
At the same time, managing the data pipeline for high FPS computer vision applications is complex. Solutions must prioritize speed without sacrificing accuracy. They must also ensure that the volume of data is a benefit, not a bottleneck, to system performance.
Here are some strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time data streaming | Instantly process and analyze incoming image data to avoid delays. |
| Data Compression | Reduce the size of image files to save storage space and speed up retrieval. |
| Edge computing | Process data on local devices to minimize latency and network impact. |
Efficient Annotation Process
A platform like Roboflow Annotate makes annotation faster and more accurate. One tool I particularly like is Label Assist, which speeds up the process by using models like Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM) to automatically annotate images. In that case, the manual work is more about checking that the annotation is accurate.
Here are some of the features that I find especially relevant:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Smart Polygon | Create polygon annotations with Meta's Segment Anything model. |
| Label Assist | Use custom models to assist with annotation. |
| Auto Label | Automatically label images with Autodistill. |
| Workflow | Use multiple models to break a complex vision task into several easier steps. |
Overview of ReductStore
Designed to store large volumes of time-series unstructured data on edge devices, ReductStore's architecture and feature set are optimized for storing and processing the continuous flow of images:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Time-Series Object Storage | Accommodates continuous data input without lag |
| Large Data Handling | Store billions of time-stamped images with AI labels and access them with low latency. |
| FIFO quotas | Prevent edge devices from running out of disk space in real time. |
| Filter data | This feature allows users to eliminate irrelevant data for faster processing. |
| Data replication | Improves disaster recovery, accessibility, and reliability by replicating critical data in the cloud. |
| Efficient Data Batching | Minimize network overhead in high latency environments. |
Annotating Data in High-FPS Environments
In high FPS environments, manually annotating every frame is often unrealistic. Instead, we need to focus on filtering key frames based on time and inference results.
By "key frames" I mean images that have already been processed by a deep learning model and whose results are important to us:
- Low model confidence: If the model is uncertain about its prediction, a low confidence score means that the image is more likely to be misclassified. We can use this information to prioritize images with low confidence scores for further review.
- Specific annotations: For example, if our model has trouble identifying red cars, we can request all red car images from the last three months for review. This allows us to focus on the most relevant data for training.
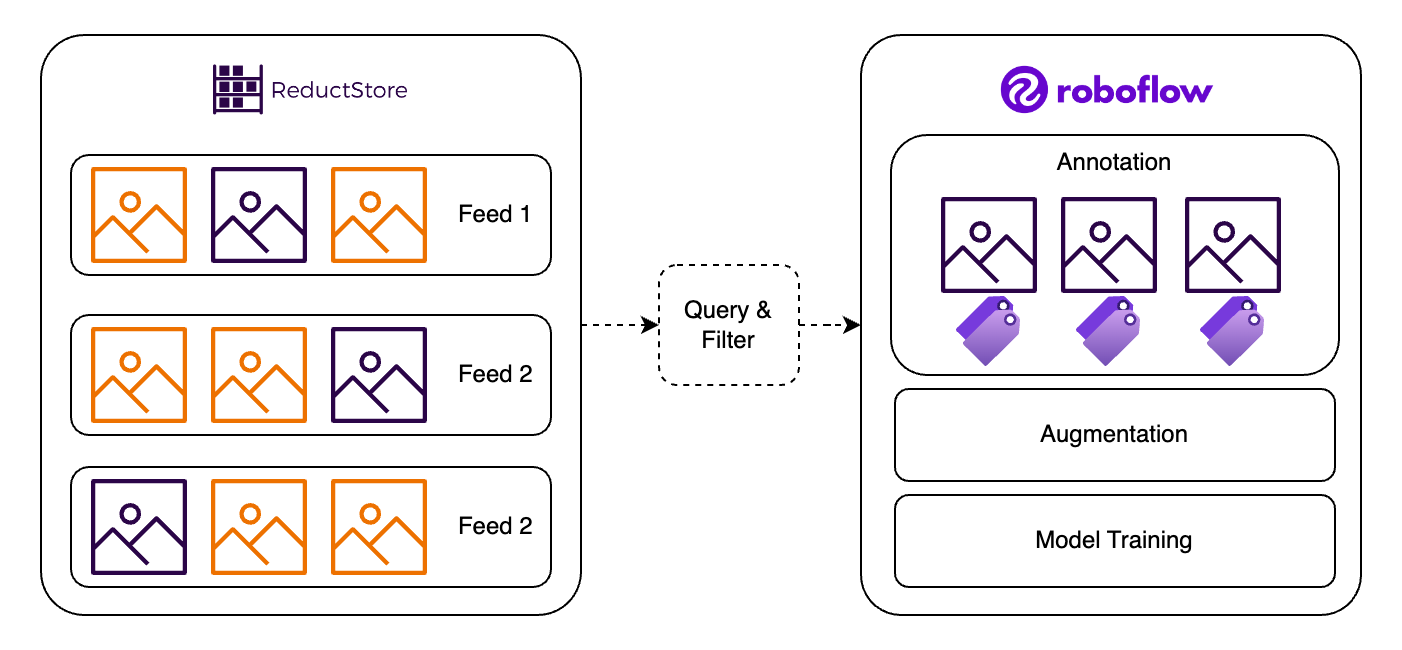
As shown in the diagram, ReductStore can filter images based on time and AI labels, so that we can focus on the most relevant frames.
Once filtered, Roboflow provides annotation tools that speed up the process of labeling these images, saving time and reducing the manual effort required for model training. This combination of filtering and fast annotation clearly helps to simplify the workflows required for high-speed vision tasks.
Conclusion
In summary, the combination of Roboflow's annotation tools and ReductStore's storage and filtering capabilities greatly improves the efficiency of training machine learning models for high-FPS computer vision applications:
- ReductStore allows you to filter and query only the most relevant images, reducing the need for manual annotation.
- Roboflow then provides fast and accurate annotation tools to label these images, speeding up the training process.
Together, these tools help you focus on the most important images, reducing the time and effort required to train your models. This is especially important in high-speed vision applications, where the volume of data can be overwhelming.
